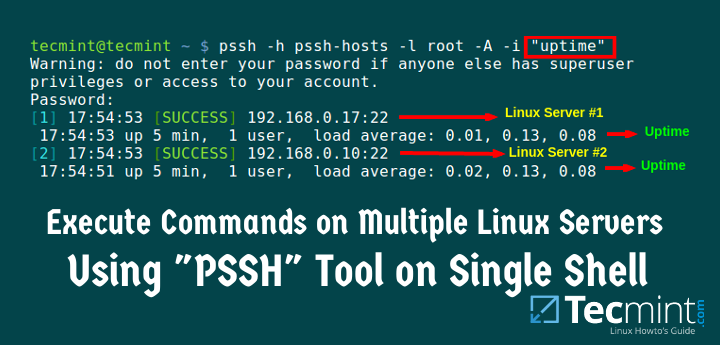
ssh command on Unix/Linux or the Mac terminal. For general information about SSH and other implementations, see the SSH protocol home page. Today we will look into JSch example tutorial. We can use JSch for creating SSH connection in java. Earlier I wrote a program to connect to remote database on SSH server. Today I am presenting a program that can be used to connect to SSH enabled server and execute shell commands. I am using JSch to connect to remote ssh server from java program. Running SSH commands in Powershell – PuTTY Method. Chances are if you have puTTY installed you will have a copy of this located in the program files folder for.
Practically every Unix and Linux system includes the ssh command. This command is used to start the SSH client program that enables secure connection to the SSH server on a remote machine. The ssh command is used from logging into the remote machine, transferring files between the two machines, and for executing commands on the remote machine.
SSH Command in Linux
The ssh command provides a secure encrypted connection between two hosts over an insecure network. This connection can also be used for terminal access, file transfers, and for tunneling other applications. Graphical X11 applications can also be run securely over SSH from a remote location.
Other SSH Commands
There are other SSH commands besides the client ssh. Each has its own page.
- ssh-keygen - creates a key pair for public key authentication
- ssh-copy-id - configures a public key as authorized on a server
- ssh-agent - agent to hold private key for single sign-on
- ssh-add - tool to add a key to the agent
- scp - file transfer client with RCP-like command interface
- sftp - file transfer client with FTP-like command interface
- sshd - OpenSSH server
Using the Linux client
Linux typically uses the OpenSSH client. The ssh command to log into a remote machine is very simple. To log in to a remote computer called sample.ssh.com, type the following command at a shell prompt:
If this is the first time you use ssh to connect to this remote machine, you will see a message like:
Type yes to continue. This will add the server to your list of known hosts (~/.ssh/known_hosts) as seen in the following message:
Each server has a host key, and the above question related to verifying and saving the host key, so that next time you connect to the server, it can verify that it actually is the same server.
Once the server connection has been established, the user is authenticated. Typically, it asks for a password. For some servers, you may be required to type in a one-time password generated by a special hardware token.
Once authentication has been accepted, you will be at the shell prompt for the remote machine.
Specifying a different user name
It is also possible to use a different username at the remote machine by entering the command as:
The above can also be expressed with the syntax:
Executing remote commands on the server
The ssh command is often also used to remotely execute commands on the remote machine without logging in to a shell prompt. The syntax for this is:
For example, to execute the command:
on host sample.ssh.com, type the following command at a shell prompt:
After authenticating to the remote server, the contents of the remote directory will be displayed, and you will return to your local shell prompt. -x Disables X11 forwarding.
SSH client configuration file
The ssh command reads its configuration from the SSH client configuration file ~/.ssh/config. For more information, see the page on SSH client configuration file.
Configuring public key authentication
To configure passwordless public key authentication, you may want to create an SSH key and set up an authorized_keys file. See the pages on ssh-keygen and ssh-copy-id for more information.
Execute Program Via Ssh Windows 10
Configuring port forwarding
Command-line options can be used to set up port forwarding. Local fowarding means that a local port (at the client computer) is tunneled to an IP address and port from the server. Remote forwarding means that a remote port (at the server computer) is forwarded to a given IP address and port from the client machine. See the page on configuring port forwarding on how to configure them.
OpenSSH also supports forwarding Unix domain sockets and IP packets from a tunnel device to establish a VPN (Virtual Private Network).

SSH command line options
Some of the most important command-line options for the OpenSSH client are:
-1 Use protocol version 1 only.
-2 Use protocol version 2 only.
-4 Use IPv4 addresses only.
-6 Use IPv6 addresses only.
-A Enable forwarding of the authentication agent connection.
-a Disable forwarding of the authentication agent connection.
-C Use data compression
-c cipher_spec Selects the cipher specification for encrypting the session.
-D [bind_address:]port Dynamic application-level port forwarding. This allocates a socket to listen to port on the local side. When a connection is made to this port, the connection is forwarded over the secure channel, and the application protocol is then used to determine where to connect to from the remote machine.
-E log_file Append debug logs to log_file instead of standard error.
-F configfile Specifies a per-user configuration file. The default for the per-user configuration file is ~/.ssh/config.
-g Allows remote hosts to connect to local forwarded ports.
-i identity_file A file from which the identity key (private key) for public key authentication is read.
-J [user@]host[:port] Connect to the target host by first making a ssh connection to the pjump host[(/iam/jump-host) and then establishing a TCP forwarding to the ultimate destination from there.
-l login_name Specifies the user to log in as on the remote machine.
-p port Port to connect to on the remote host.
-q Quiet mode.
-V Display the version number.
-v Verbose mode.
-X Enables X11 forwarding.
A little history
SSH replaced several older commands and protocols in Unix and Linux the 1990s. The include telnet, rlogin, and rsh.
Execute Program Via Ssh Download
SSH runs at TCP/IP port 22. This is right between ftp and telnet, which are 20 years older. Read the story of how SSH got port 22.
The following video summarizes how and why SSH was originally developed.
silent ssh is setup from server A to server B (and some 500 other servers)
I have written a script on server A (shell and perl) that I want to execute via ssh on server B (and the other 500 servers).Is this possible ? I am able to run commands using silent ssh but not sure how to run entire scripts.
5 Answers
If Server A is a Unix/Linux-based system, you can use:
You shouldn't have to copy the script to the remote server to run it.
Since silent ssh is already setup is already setup as you say, I would scp the file the file and execute it locally
i.e:
Running the script on client site is less error prone than parsing it with < << operators.
Something similar to the script above should do most of the work for you (hopefully all). Also it will keep track of anything ( &> forwards error messages) that went wrong so you know which IP addresses you need to attend manually.
Above is a script I found with a little searching about and modified a bit to show an example of usage and example of using keys for connections as the OP stated that it would be run on many other servers. This script also is coded such that you may pass arguments to the local script and specify the program that the server should use to recieve the script's commands; ie you may tell your server to use perl or python or java... and then give it that related script :-DThe source I found the above script is hard coded into it's comments such that copy/past will still allow you years latter to find the original authors ;-)
Happy networking to you all.
Ssh Execute Command And Exit
You can execute remote commands over ssh like
ssh user@serverA /path/to/your/script
 deagh
deagh